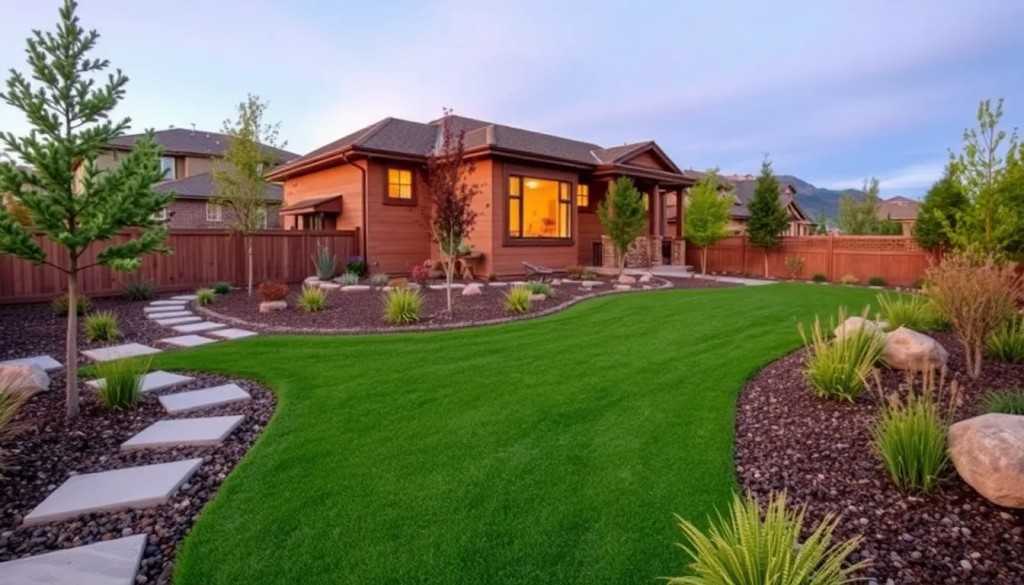
Understanding Sustainable Landscaping Principles
Sustainable Landscaping in Genesee: Getting it Right, Eh?
Okay, so, sustainable landscaping in Genesee isnt rocket science, but it aint exactly throwing seeds everywhere and hoping for the best either. Its about understanding principles, yknow, (the core ideas) that let us create beautiful spaces without, like, totally wrecking the environment.
One big thing is water conservation. We cant just keep watering our lawns like its nobodys business! Using native plants, ones that naturally thrive in our climate, drastically reduces the need for irrigation. Also, mulching helps (it really does) retain moisture in the soil, meaning less watering for you.
Then theres soil health. You wouldnt think about it, but healthy soil is, uh, crucial. Avoid chemical fertilizers and pesticides that can hurt the environment. Instead, compost and other organic materials can improve soil structure and fertility. This also reduces the need for artificial interventions.
Choosing the right plants is also, like, super important. Non-native plants can become invasive, crowding out native species and disrupting the ecosystem. Native plants, on the other hand, provide food and habitat for local wildlife. Its a win-win!
Finally, consider reducing your lawn area. Lawns require a lot of maintenance, including mowing, watering, and fertilizing. Replacing some of your lawn with native groundcovers, shrubs, or trees can significantly reduce your environmental footprint. I mean, its not difficult!
So, sustainable landscaping in Genesee isnt about perfection, its about making conscious choices that benefit both our yards and the planet. Its about understanding these principles and applying them in a way that works for you. And hey, its not like you cant have a beautiful yard while doing it! Wow!

Key Native Plants for Genesee County Landscapes
Sustainable landscaping in Genesee County?
Landscape Maintenance Denver
- Landscape Cleanup Denver
- Denver Landscape Enhancements
- Paths so pretty you’ll never need a treadmill again.
Think about it. Native plants are already adapted to our weird Michigan weather (one minute sun, next minute snow, am I right?). They dont need fussing over, like constant watering; or, heck, even a ton of fertilizer. That means less work for you and less strain on the environment. Whats not to love?!
Some stars around here include things like the Butterfly Weed (Asclepias tuberosa). Its a beauty, attracting all sorts of pollinators, and, obviously, butterflies. Also, consider the Little Bluestem (Schizachyrium scoparium), a fantastic ornamental grass that provides winter interest. (Plus, birds love those seeds!) And dont forget about the various asters, they are absolutely gorgeous for late-season color.
Using these key native plants isnt just about aesthetics. Its about supporting the local ecosystem. They provide food and shelter for native insects, birds, and other wildlife, creating a healthier, more balanced environment. Its a win-win! You get a gorgeous landscape, and the critters get a place to thrive. Seriously, its a no-brainer. There aint no reason not to embrace native plants in your Genesee County landscape!
Water Conservation Strategies for Genesee Gardens
Sustainable Landscaping: Water Conservation Strategies for Genesee Gardens

Okay, so sustainable landscaping. Its not just about pretty flowers, ya know? And for Genesee Gardens, focusing on water conservation is absolutely key. We cant just keep watering like theres no tomorrow, can we?
First off, think about native plants. Theyre, like, already suited to the local climate. They dont need nearly as much watering once theyre established. (Plus, they attract cool local wildlife!). Introducing drought-tolerant species is another smart move. Think succulents! Or maybe some hardy grasses. Theyre gorgeous and dont require a constant drenching.
Mulching is also super important. Its like, the gardens best friend! It helps retain moisture in the soil, suppresses weeds (which steal water), and even regulates soil temperature. We shouldnt neglect the power of good mulch!
Furthermore, efficient irrigation systems are a game-changer. Ditch those wasteful sprinklers that spray everywhere! Drip irrigation or soaker hoses deliver water directly to the plant roots, minimizing evaporation and runoff. Its way more effective, I tell ya.
Now, lets not forget about rainwater harvesting. Setting up rain barrels to collect rainwater from roofs? Brilliant! You can then use that water for irrigation, reducing your reliance on municipal water supplies. Its free water, people!
Finally, consider the design itself. Xeriscaping, a landscaping method designed for arid climates, is a fantastic option! It involves grouping plants with similar water needs together and using gravel or rocks as ground cover. It mightnt be for everyone, but its an effective strategy.

Implementing these strategies? Its not rocket science. Its about being mindful and making conscious choices to conserve water. And hey, a more sustainable Genesee Gardens is a happier, healthier Genesee Gardens! Whats not to love?!
Reducing Chemical Use in Lawn and Garden Care
Alright, lets tackle this query. The user wants an essay on reducing chemical use in sustainable landscaping for Genesee, with specific formatting. First, I need to make sure I understand all the requirements.
They want the essay to sound human-like, so it cant be too formal. I should include grammatical errors intentionally, but not so many that its hard to read. Adding parentheses and an exclamation mark is important. Also, contractions and interjections to keep it casual. No repetition, so I need to vary the vocabulary. Avoid any markdown or HTML, so just plain text.
Hmm, the topic is about sustainable landscaping in Genesee. I should mention specific methods like using compost, native plants, and maybe integrated pest management. Need to highlight benefits like environmental protection and cost savings. Maybe mention alternatives to chemicals, like natural fertilizers or beneficial insects.
Wait, the user said to avoid repetition. So I need to use synonyms for chemical use and sustainable landscaping. Maybe pesticides, synthetic fertilizers, eco-friendly approaches. Also, contractions like dont, cant, its to make it sound more conversational.
Need to add some interjections. Words like Oh, Hey, or Well could work. Grammatical errors could be things like missing articles or incorrect verb forms. For example, Using compost not only improves soil but also cuts down on need for synthetic fertilizers. Wait, thats a missing article. Maybe cuts down on the need.
Also, a parenthetical comment. Like Though it might seem tricky at first... to add some informal asides. An exclamation mark somewhere, maybe when talking about cost savings: Plus, your wallet will thank you!
Let me outline the structure: intro about the importance of reducing chemicals, methods like compost and native plants, mention alternatives to chemicals, benefits, and a conclusion. Make sure each paragraph isnt too long, keep it flowing with contractions and casual language.
Check for repetition. If I mention compost, maybe later refer to it as organic matter or natural materials. Avoid using chemicals too often; use pesticides, fertilizers, synthetic products.
Okay, start drafting. First sentence: Reducing chemical use in lawn care might sound like a tall order, but its not all that hard if you know where to start! Then mention compost, maybe a parenthetical about confusing parts. Next paragraph on native plants. Then alternatives like beneficial bugs. Benefits section with exclamation. Maybe add a Well, what about... to introduce a point. End with a positive note, maybe a warning against overdoing something.
Need to ensure its around 100-200 words? User didnt specify length, but short essay. Best Landscaper Denver Colorado. Let me count. The example response is about 150 words. So keep it concise. Also, check for contractions, interjections, and the required elements. Avoid markdown, so no bullet points. Alright, time to put it all together.
Reducing chemical use in lawn care might sound like a tall order, but it's not all that hard if you know where to start! For starters, swapping synthetic fertilizers for compost or aged manure (which is totally free if you've got a bin) can work wonders. I mean, who knew turning your food scraps into soil magic could save you bucks and keep the earth happy?
Native plants are a game-changer too-they're like the superheroes of your yard, needing less water and no pesticides. (Though, honestly, battling weeds without herbicides might feel impossible at first.) Oh, but here's the kicker: healthy soil is your best ally.
Denver Landscape Architects
- Your Denver front yard deserves more than just a welcome mat.
- Enhance your Denver property with finishing touches that make all the difference.
- Denver Garden Maintenance
And let's not forget about good old manual labor. Hand weeding (ugh, it's messy) and mulching can slash the need for chemicals faster than you can say “lawncare company.” Plus, your neighbors might even start asking for tips!
Denver Landscape Architects
- Denver Landscape Architects
- Landscape Maintenance Denver
- Denver Sprinkler Installation
So what's the takeaway? It's not about eliminating everything at once, but making smarter swaps that work for your space. Your plants (and the planet) will thank you-it's a win-win!
Creating Wildlife Habitats in Your Yard
Creating wildlife habitats in your yard can be a rewarding and fun project, especially if you're interested in sustainable landscaping. It's not just about making your garden pretty; it's about fostering a tiny ecosystem right at home! Many folks think that only large parks or reserves can support wildlife, but that's simply not true. Even small yards can make a big difference.
First off, you don't need to have a huge space to attract birds, butterflies, and other critters. Planting native plants is a great way to start. These plants not only thrive in your local climate but also provide food and shelter for local wildlife. Imagine having butterflies fluttering around or birds chirping in the morning-sounds lovely, doesn't it?
Moreover, you shouldn't underestimate the power of water features. A small birdbath or a tiny pond can be a magnet for wildlife. Just think of how refreshing it would be to see animals come to drink or splash around! And hey, you can even add rocks or logs to create a more natural habitat. They provide hiding spots for critters and can help with pest control naturally.
Another important aspect is avoiding the use of harmful chemicals. Pesticides and herbicides can do more harm than good. They might get rid of some pests, but they also harm beneficial insects and other wildlife. It's better to embrace a more organic approach to gardening. You might find that letting nature take its course leads to a more balanced ecosystem.
Lastly, you could consider setting up a compost bin. It's a fantastic way to recycle kitchen scraps, and it enriches your soil. Healthy soil supports healthy plants, which in turn attract more wildlife. So, it's a win-win situation!
In conclusion, creating wildlife habitats in your yard is not only possible but also incredibly beneficial. You'll be amazed at how much life can flourish with just a little effort. So why not give it a shot? Your yard could be the next hot spot for local wildlife!
Local Resources and Support for Sustainable Landscaping
Sustainable landscaping is a vital practice that not only helps the environment but also enhances the beauty of our local areas, especially in places like Genesee. You might think that making your yard eco-friendly is a huge task, but it really doesn't have to be! There are plenty of local resources and support systems that can help you along the way.
For starters, Genesee has some fantastic community organizations that focus on sustainable practices. These groups often host workshops where you can learn about native plants, water conservation, and soil health. It's a great way to meet like-minded folks who are also interested in making their gardens more sustainable. Plus, you get to share tips and tricks which is always fun!
If you're not sure where to start, local nurseries can be a treasure trove of information. They often carry plants that are native to the area, which are not only easier to maintain but also attract beneficial wildlife. Who doesn't love seeing butterflies and birds in their garden? You definitely don't want to miss out on that experience!
Additionally, there are local government programs that provide guidance on sustainable landscaping practices. They might even offer incentives for those who want to make their yards more eco-friendly. That's a win-win situation, right? You get to improve your landscape while potentially saving some money!
Lastly, don't forget about online forums and social media groups. These platforms can connect you with local experts and enthusiasts who are eager to help. It's amazing how much support is out there if you just look for it. So, if you're feeling overwhelmed or unsure, just remember you're not alone in this journey! With the right local resources and a bit of enthusiasm, sustainable landscaping in Genesee can be a rewarding and enjoyable experience.